READY FOR DOWNLOAD
Your Industry 4.0 Infrastructure
Dealing with the services of blockchain is worthwhile for industrial companies if they concentrate on the right starting points. Six points to consider, explains Dr. Markus Jostock, Founder & Managing Director of ARXUM.
CERTAINTY 1: The blockchain is not a footnote in the history of technology
In many fields, the use of blockchain technology is still in its infancy. However, due to the degree of maturity they have so far achieved in the financial sector, one thing is already certain: the blockchain will remain. Especially in the management of supply chain and production processes, it offers advantages that have to be implemented in other systems for a long time. Especially when hedging transactions, two advantages ensure that the blockchain is attractive to the industry in the long term. Firstly, it prevents the falsification of information in IT systems; secondly, it creates a protected information transparency at all stations of the value stream: for example, if a machine is connected to the blockchain in production, it can document the exact numbers produced and other process parameters for each product in a forgery-proof manner.
CERTAINTY 2: Smart Contracts coordinate the process steps in the supply chain
In this way, the machine can then communicate the completion of a component to the customer or the next station in the supply chain. Instead of connecting several different ERP / IT systems with each other under high time and cost expenditure, all participants only access one blockchain interface, which contains all externally relevant order data. “Smart Contracts”, which work on the basis of protocols such as Ethereum, Æternity, EOS, NEO, Stellar or Iota, carry out many actions automatically. For example, they issue shipping orders to logistics service providers when a certain number of items is reached, so that the collection and delivery of the finished goods can be coordinated much more precisely and reliably.
CERTAINTY 3: Autonomous objects carry an individual life cycle signature
Of course, Smart Contracts are not limited to machines, but could in future provide every physical object in the supply chain with a blockchain framework contract. It contains the most important information about the product and automates process steps at the same time. Goods are thus transformed into “Distributed Autonomous Objects” (DAO). By means of “function orders”, DAO can also require suppliers to continuously update information such as measured values, results from quality controls or the delivery status of the product. For this purpose, not the complete data, but only so-called “hash values”, simple “fingerprints” of the data, are exchanged, which additionally increases security. If the manufacturer permits, not only suppliers and partners, but also end customers, could use this signature to trace the complete “life cycle” of a product on a smartphone or computer.
CERTAINTY 4: The human interface remains a risk zone
This transparency significantly improves control and compliance with quality standards, compliance guidelines and social governance standards. As soon as companies link corresponding obligations with forgery-proof blockchain technologies, they can no longer pay lip service. Audits of supplier conglomerates, for example to control quality and work standards, can thus also be carried out faster, more spontaneously and with clearer results - if one really wants to use this knowledge. However, blockchain technologies do not release people from any control and responsibility. Finally, you cannot distinguish whether the data entered is correct or manipulated. All interfaces between the blockchain and the “real” world, where people decide on the collection and transmission of information, thus remain risk zones for actual, complete transparency.
CERTAINTY 5: Blockchain Oracles validate information
At the same time, blockchain is equipping companies with a new arsenal of methods to detect manipulations in good time. Since blockchains themselves do not access information outside their chain, they require a separate instance to check whether the conditions of the “smart contracts” are met as agreed. One such instance is “Blockchain Oracles”, which provide external information about the real world, such as payment transactions, price or weather changes in the blockchain. For example, if a certain value is reached for stock exchange raw material prices, the predefined algorithms in the smart contract can trigger price comparisons with suppliers. By using multiple sources of information, organizations try to achieve the best possible validity of the information.
CERTAINTY 6: Batch size 1 is possible at mass production conditions
Bicycles with the perfect frame height, tailor-made shirts or individually designed watches: Blockchain technology opens up realistic options for the consumer goods industry to produce very individual products at mass production costs. However, the prerequisite is a continuous digitization of all process steps from the collection of the first customer data to the delivery of the goods.
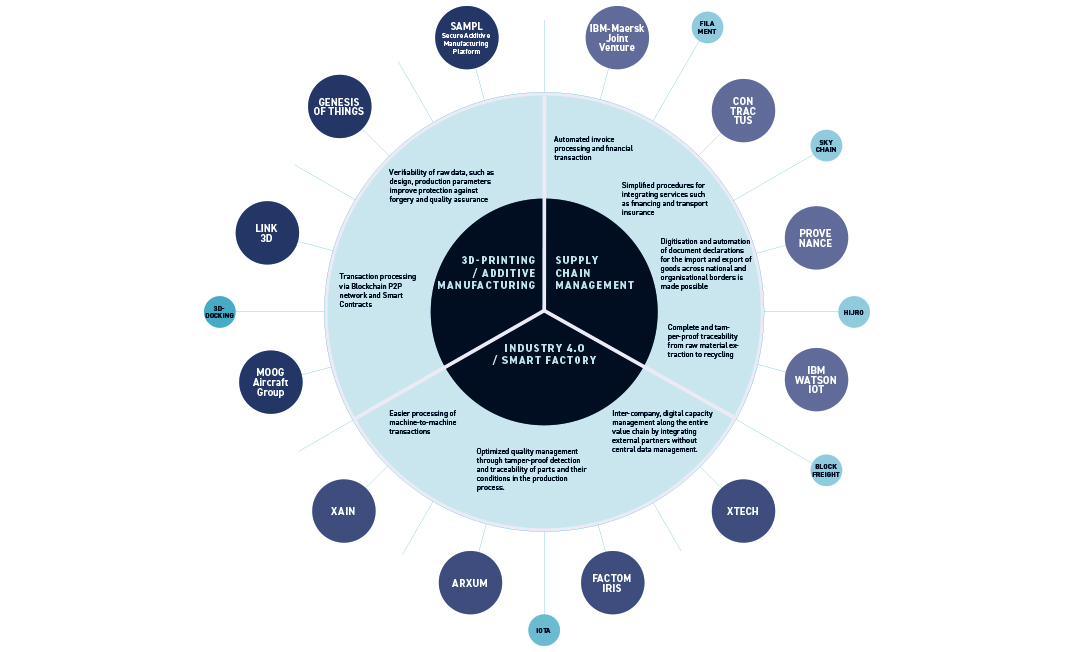
ARXUM WAS FOUNDED BY A TEAM OF EXPERIENCED INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERS
The company solves challenges in the manufacturing industry by connecting manufacturers, suppliers and customers in a blockchain-based network. Data can thus be transferred effortlessly between users and machines, enabling customized production at the price of mass production.
